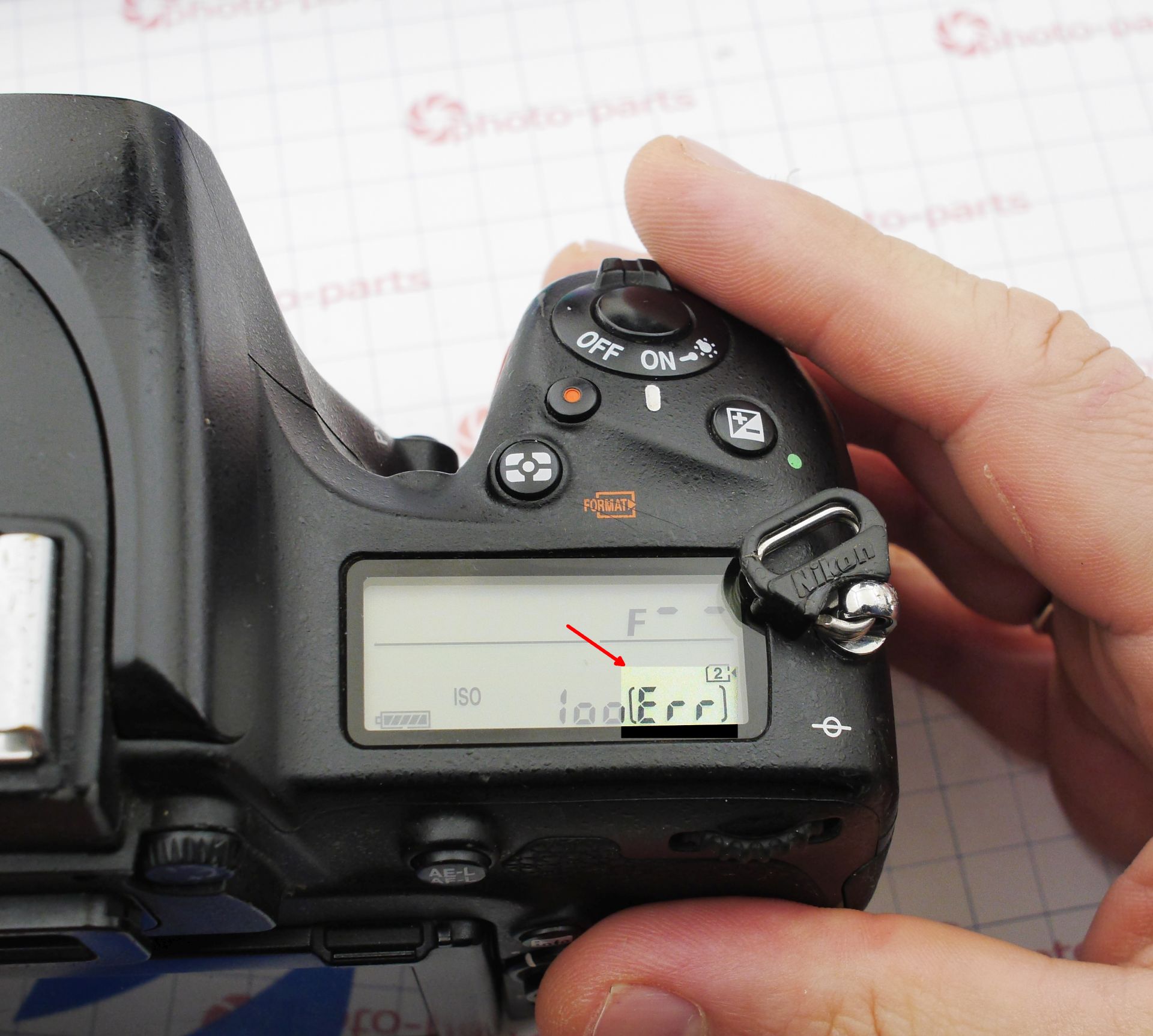
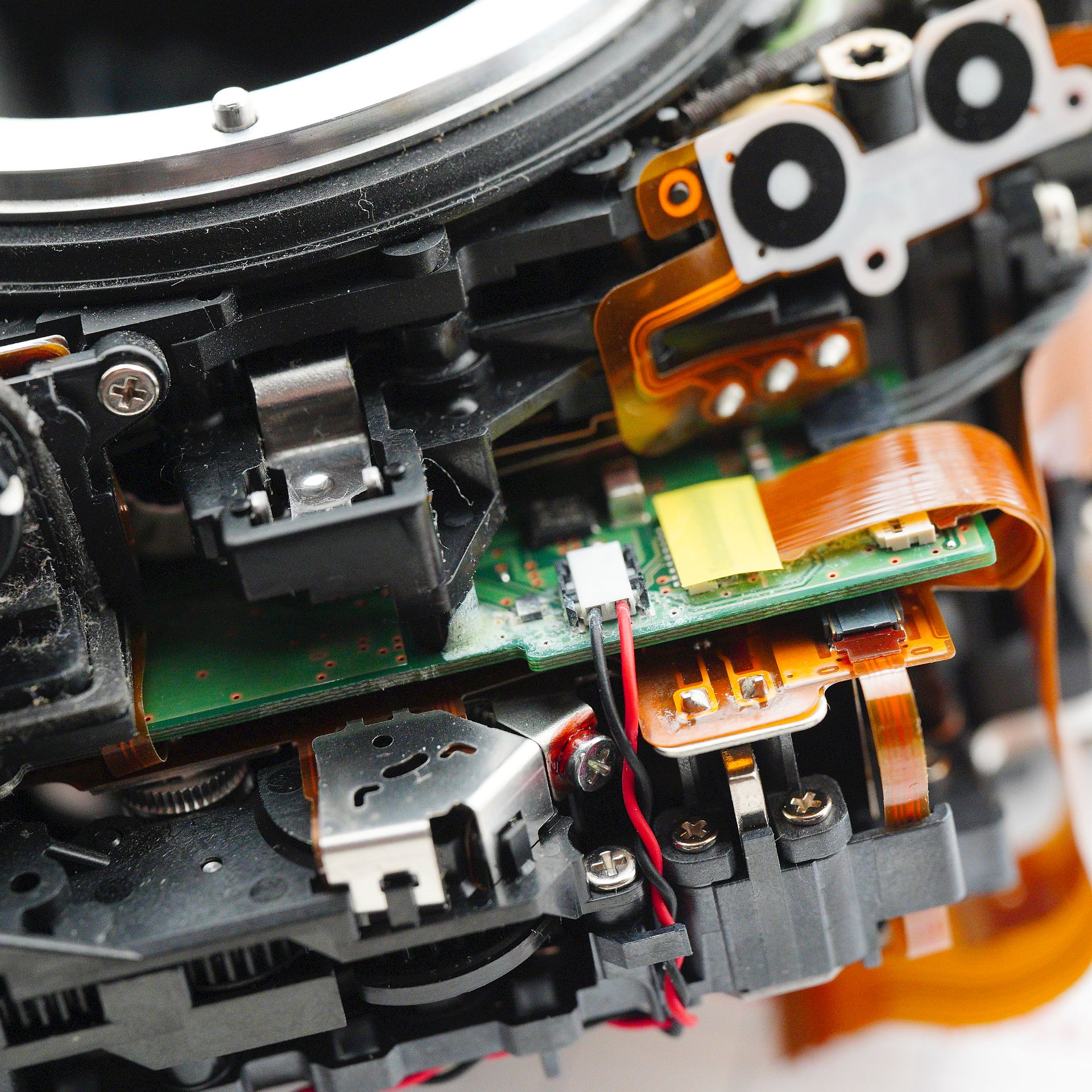
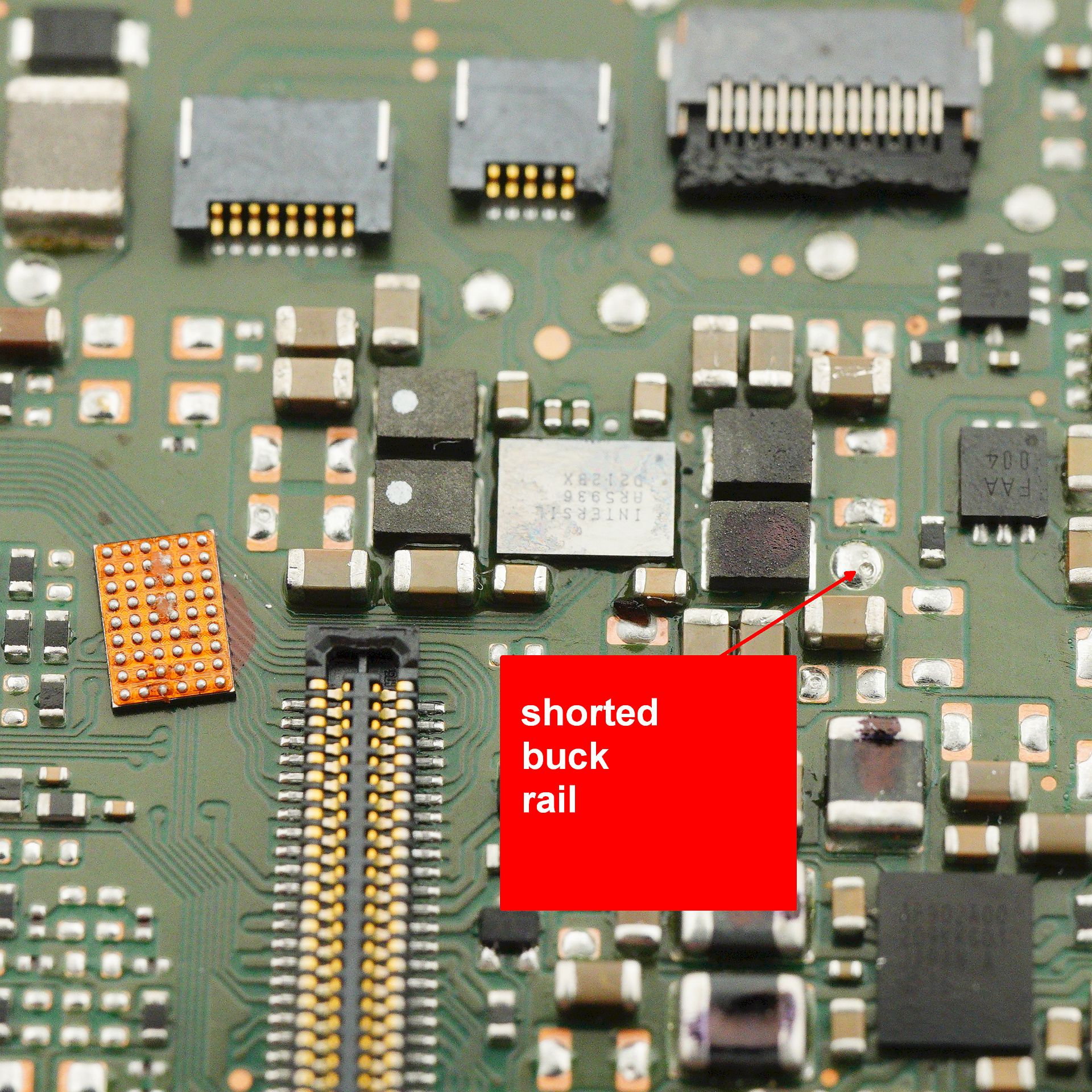
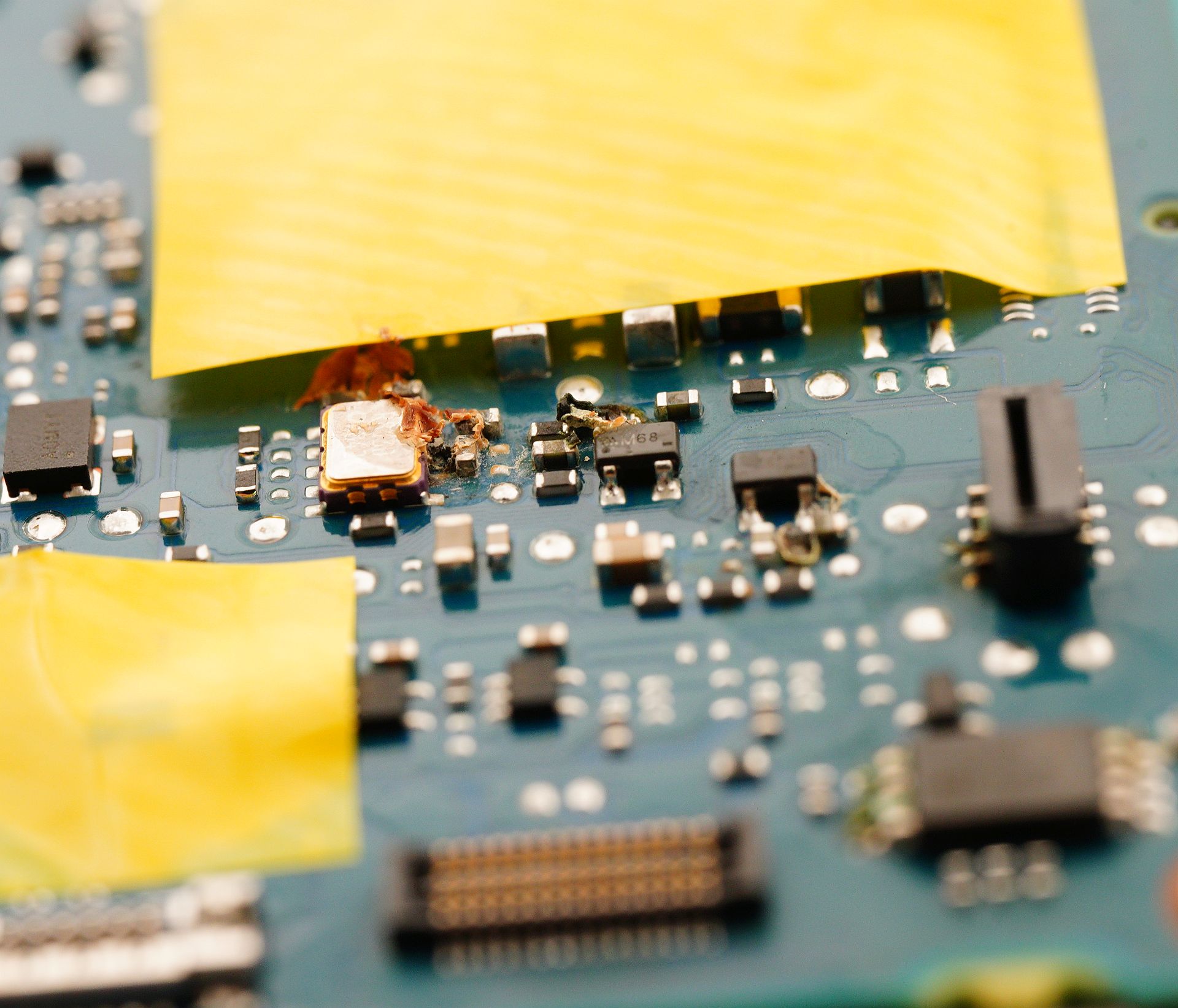
The most ordinary type of repair - a true "walk-in job," as repair technicians like to say. Just replace a faulty memory card slot: minimal disassembly, a bit of soldering - and the camera is saved. However, even in such a simple repair, there are a few nuances that can easily turn fatal for the camera. Our patient: Nikon D750, which, even without a memory card inserted, shows the "err" message instead of the frame counter. The camera is unusable - the shutter is locked, even if you try to
-
-
How often have you thought about the "ultrasonic sensor cleaning” technology that’s present in almost every modern camera? Probably not very often — after all, its work is barely noticeable, if not downright invisible. The idea is simple: when the camera powers off, the outer glass of the sensor filter vibrates at high frequency, shaking off dust (in theory). In practice, this technology is far from a cure-all - micro-vibrations of the glass do little against heavily charged dust, sticky
-
By today's standards, the Nikon D780 is supposedly hopelessly outdated (of course not!), but I've never had a chance to look inside before. This model somehow got lost between the super-popular D750 and D850, and even spare parts for it were not eagerly sold. So when I was asked about the possibility of repairing one, I replied with great enthusiasm. The problem, as described by the owner, was also unusual: one not-so-fine day, the camera simply stopped taking pictures. Pressing the shutter
-
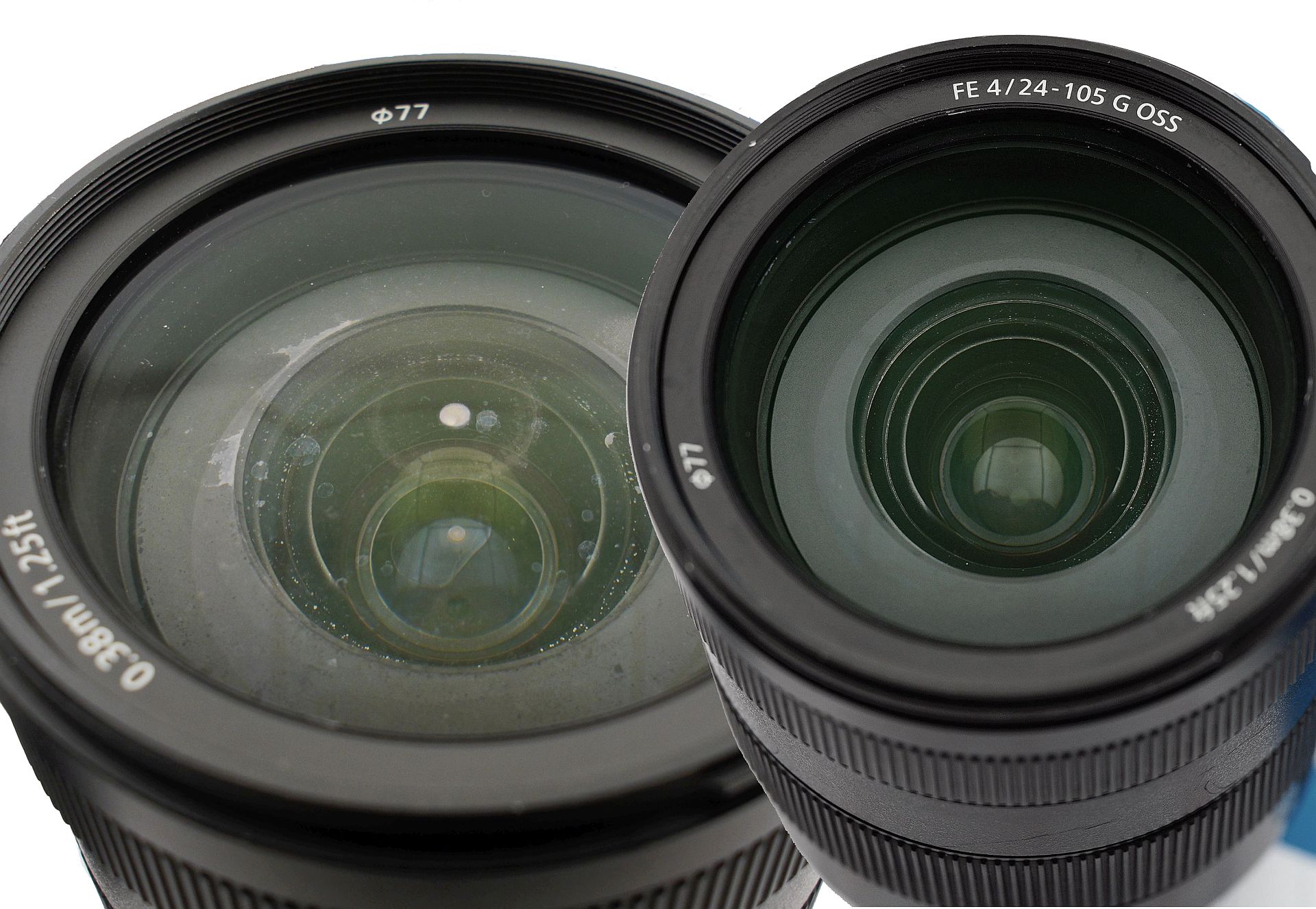
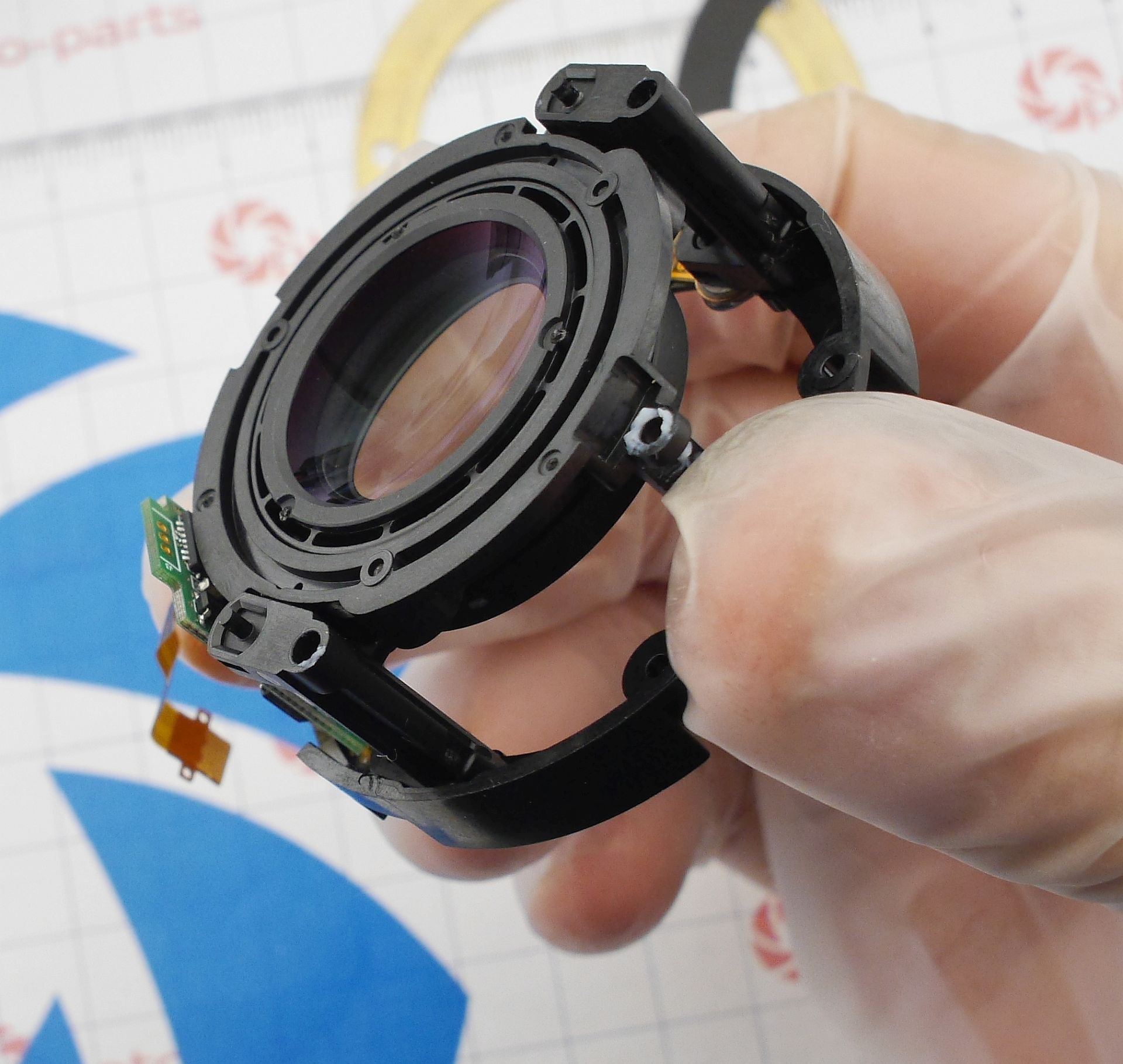
I often see two opposite cases in lens repair: the optics are in perfect condition, but something prevents the lens from working (broken autofocus, falling apart enclosure, and so on), or - everything seems to work, but the optics are in a terrible state. Today - about the second case. The Sony FE 24-105mm G OSS lens was fully submerged in some body of water, dried out, and remained functional (the aperture, stabilizer and focus all still work), but with awful stains everywhere. I'm facing a
-
Variations in the final product are nothing unusual. In mass production, reliability gets refined, costs are optimized (though sometimes one comes at the expense of the other), and engineers make small tweaks to the design along the way. I can name several pieces of photographic gear where identical external appearance hides very different internals. But this time, Sony has outdone everyone — two completely different lenses hiding under the exact same nameplate! That’s a bit of a spoiler,
-
The title of this post can’t possibly capture the full extent of frustration that comes with repairing modern Canon cameras. We’ve got everything here: serious damage from minor water ingress, excessive reliance on proprietary ICs, and complete unavailability of component-level spare parts. Things are so bad that if you try to Google the part number of the faulty chip, you’ll find exactly this page, plus maybe one more - also from my own site. This Canon EOS R10 arrived with a
-
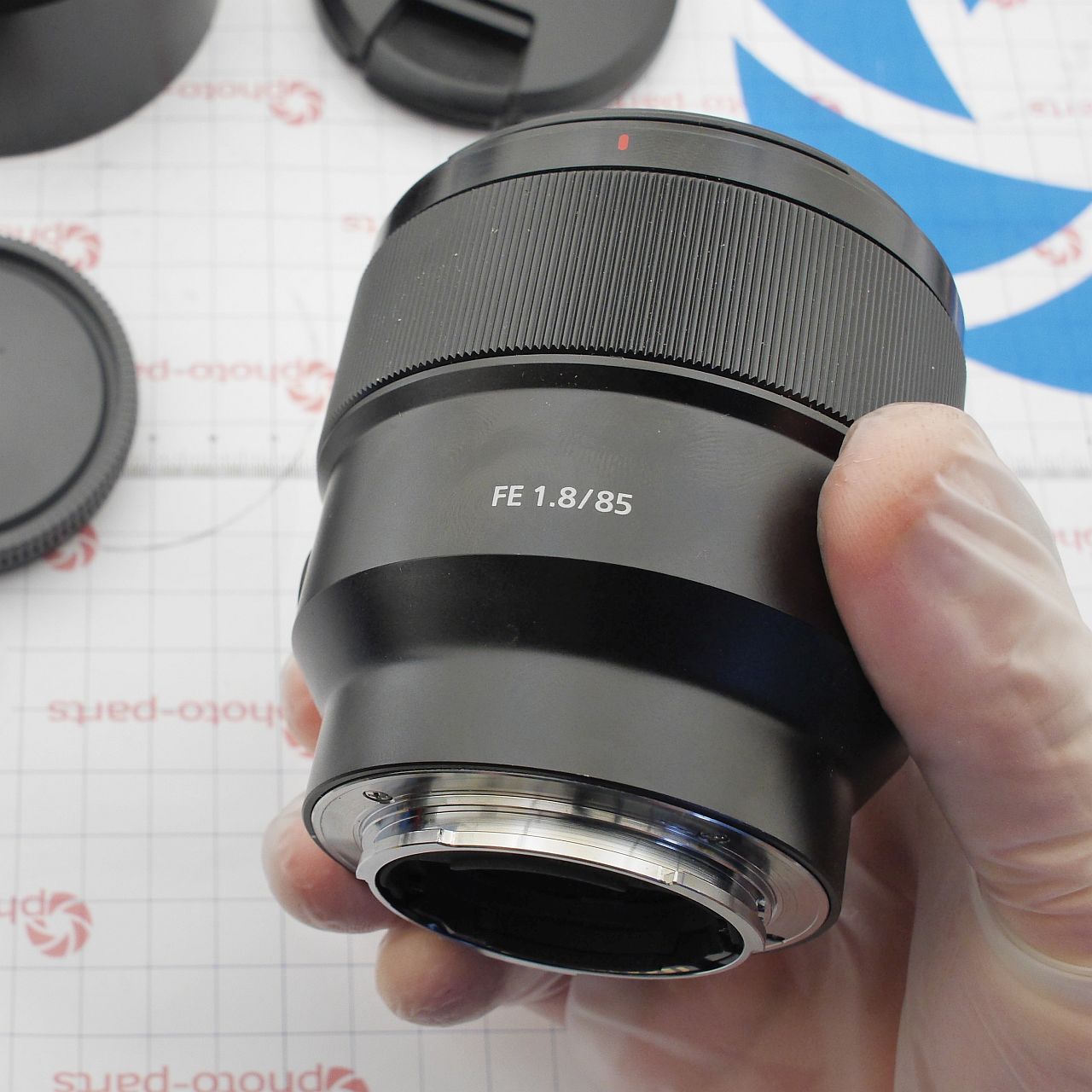
The first number that comes to mind when someone says "portrait lens" is undeniably 85mm. If you’ve got deep pockets and strong arms, you go for the f/1.4 (or even f/1.2); for less demanding photographers, there's f/1.8. Every major manufacturer offers a mass-market 85/1.8, and for example, the Canon 85mm f/1.8 USM is a true repair classic - often seen with worn optical encoders or a finicky aperture. This is our first time opening up the Sony FE 85mm f/1.8 - and we're excited to share it.
-
The Canon 6D Mark II needs no introduction - an extremely popular full-frame camera for enthusiasts (in the past, at least). Somehow, I only got around to writing about its repair now - but better late than never. Today's patient arrived with the description: "dead as a dodo." I'm not quite sure what the owner meant by that, but the camera truly showed no signs of life. In this article: disassembly, interesting damage caused by an unknown liquid, and an unexpected culprit behind the failure.
-
Fast autofocus lenses from the South Korean company Samyang are extremely interesting and slightly underrated. The company has journeyed from fully manual budget lenses to fully compatible autofocus models, and they've succeeded. Modern AF lenses don't just have autofocus; they're equipped with “trendy” ultrasonic motors of their own design. Considering the excellent image quality, I'd place them alongside both branded primes and general-purpose zooms. Of course, there's a bit of hardware
-
I can accept "natural" damage without complaint. Water ate half the camera? Alright, it happens. A drop cracked the shell? Fair enough. But when some butterfingered “technician” makes things worse inside - I get furious. This camera arrived with the complaint: “the display doesn’t work, it reboots after language selection, and overall it’s not in great shape.” Turns out - even that was a lie. The camera was completely dead, zero reaction to the power lever. Let’s begin the